- Direct current.
Between the terminals of a battery, there is a continuous, stable flow of energy. This is called direct current.
- Alternating current.
The variation of any electrical parameter over a period of time is an electric signal. The tension or voltage of domestic electricity is an alternating signal because it alternates between positive and negative values. Alternating current is produced by generators, such as the ones in large electrical generating stations.
- The efficiency of alternating current.
The average power of alternating current is equal to the direct current that is needed to produce the same effect.
- Transformers.
Transformers consist of two windings made a cooper wire. If we apply an alternating current to one of them, it will produce a certain voltage in the other. The value will depend on the number of times that the cooper wire has been wrapped around each winding.
Saturday, 25 March 2017
TYPES OF CIRCUITS
- Series circuit.
In a series circuit the current flows through all the elements. The total voltage is the sum of the tensions at the end of each element.
To calculate the total resistance of a circuit, we add the resistance values.
- Parallel circuit.
In a parallel circuit, the various components share the same input and output. If identical batteries are connected in parallel, the voltage of the circuit will not increase.
- Combination circuit.
A combination circuit has some elements connected in series and other elements connected in parallel.
The current remains constant between elements that are connected in series, at the same time, the voltage remains constant between elements that are connected in parallel.
In a series circuit the current flows through all the elements. The total voltage is the sum of the tensions at the end of each element.
To calculate the total resistance of a circuit, we add the resistance values.
- Parallel circuit.
In a parallel circuit, the various components share the same input and output. If identical batteries are connected in parallel, the voltage of the circuit will not increase.
- Combination circuit.
A combination circuit has some elements connected in series and other elements connected in parallel.
The current remains constant between elements that are connected in series, at the same time, the voltage remains constant between elements that are connected in parallel.
Thursday, 16 March 2017
ELECTRICAL QUANTITIES
- Voltage or potential difference.
The amount of energy that generator can transfer the electrons depends on its voltage (V). This is measured in volts (V).
We can use a voltmeter to measure the voltage. This device has two wires that must be connected in parallel to the element that we are checking.
- Measuring electric current.
Electric current (I) is the charge or number of electrons that flow through the cross-section of a conductor every second.
I = Q/t
Electric current is measured in amperes or amps (A).
We can use an ammeter to measure electric current. This instrument is connected in series, so that all the electrons must pass through it.
- Electrical resistance: Ohm's Law.
The resistance (R) of a material is equal to the voltage divided by the intensity of the electric current wich travels through the material. Is called Ohm's Law, can be expressed as follows: R = V/I
The Ohm's Law has two forms: V = R x I and I = V/R
- Electrical energy and power.
· Electrical energy.
If an electrical current (I) flows at a particular tension (V) for a certain amount of time (t), we can calculate the energy (E) that is consumed: E = V x I x t
This electrical energy is measured in joules (J).
· Electric power.
If an electric current (I) flows at a particular tension (V), we can calculate the power (P) that is consumed: P = V x I
Electric power is measured in watts (W) or kilowatts (kW).
We can calculate the electrical energy that it consumes over a certain amount of time:
E = P x t
The amount of energy that generator can transfer the electrons depends on its voltage (V). This is measured in volts (V).
We can use a voltmeter to measure the voltage. This device has two wires that must be connected in parallel to the element that we are checking.
- Measuring electric current.
Electric current (I) is the charge or number of electrons that flow through the cross-section of a conductor every second.
I = Q/t
Electric current is measured in amperes or amps (A).
We can use an ammeter to measure electric current. This instrument is connected in series, so that all the electrons must pass through it.
- Electrical resistance: Ohm's Law.
The resistance (R) of a material is equal to the voltage divided by the intensity of the electric current wich travels through the material. Is called Ohm's Law, can be expressed as follows: R = V/I
The Ohm's Law has two forms: V = R x I and I = V/R
- Electrical energy and power.
· Electrical energy.
If an electrical current (I) flows at a particular tension (V) for a certain amount of time (t), we can calculate the energy (E) that is consumed: E = V x I x t
This electrical energy is measured in joules (J).
· Electric power.
If an electric current (I) flows at a particular tension (V), we can calculate the power (P) that is consumed: P = V x I
Electric power is measured in watts (W) or kilowatts (kW).
We can calculate the electrical energy that it consumes over a certain amount of time:
E = P x t
ELECTRIC CIRCUIT
An electric circuit is a pathway for the flow of electrons. Electric current is a continuous flow of electrons through a circuit.
- Parts of an electric circuit.
· Generators provide the energy that electrons need in order to move.
· Loads are devices that transform electrical energy into other types of energy that we can use:
~ Light bulbs: produce light.
~ Motors: produce movement.
~ Resistors: produce heat.
~ Bells: produce sound.
· Switching devices are used to direct and interrupt the flow of electic current.
~ Switches: permit or interrupt the flow of electric current.
~ Push buttons: are switches that only function when they are pushed.
~ 3-way switches: permit the flow of electric current through one section of a circuit, while interrupting the flow through another branch.
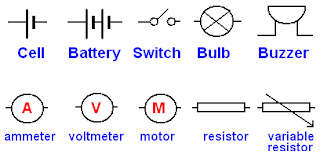
- Diagrams and symbols.
- Parts of an electric circuit.
· Generators provide the energy that electrons need in order to move.
· Loads are devices that transform electrical energy into other types of energy that we can use:
~ Light bulbs: produce light.
~ Motors: produce movement.
~ Resistors: produce heat.
~ Bells: produce sound.
· Switching devices are used to direct and interrupt the flow of electic current.
~ Switches: permit or interrupt the flow of electric current.
~ Push buttons: are switches that only function when they are pushed.
~ 3-way switches: permit the flow of electric current through one section of a circuit, while interrupting the flow through another branch.
- Diagrams and symbols.
Wednesday, 15 March 2017
HOW CAN WE SAVE ENERGY?
- Energy efficiency.
An energy-efficient device requires less energy to perform the same work.
· Lighting: we can replace traditional incandescent lightbulbs with LED bulbs.
· Domestic appliances: we can reduce the consumption by unplugging devices that we are not using.
· Air conditioning and heating: we use a lot of energy to keep our homes at a confortable temperature, but there are ways we can be more efficient, for example, in winter we can put on warm jumper instead of wearing a T-shirt.
· Transport: the best way to consume less energy is to use public transport or to travel with other people when going long distances.
- Recycling.
Our consumption of manufactured products generates waste and uses energy. We can reduce these negative effects by recycling as much as possible. Recycling saves water and reduces the emission of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
- Positive impact.
Energy efficiency haas a beneficial effect on the environment.
When we consume less energy, it helps o reduce the greenhouse effect and climate change. Renewable energy sources are essential for solving our environmental problems.
An energy-efficient device requires less energy to perform the same work.
· Lighting: we can replace traditional incandescent lightbulbs with LED bulbs.
· Domestic appliances: we can reduce the consumption by unplugging devices that we are not using.
· Air conditioning and heating: we use a lot of energy to keep our homes at a confortable temperature, but there are ways we can be more efficient, for example, in winter we can put on warm jumper instead of wearing a T-shirt.
· Transport: the best way to consume less energy is to use public transport or to travel with other people when going long distances.
- Recycling.
Our consumption of manufactured products generates waste and uses energy. We can reduce these negative effects by recycling as much as possible. Recycling saves water and reduces the emission of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
- Positive impact.
Energy efficiency haas a beneficial effect on the environment.
When we consume less energy, it helps o reduce the greenhouse effect and climate change. Renewable energy sources are essential for solving our environmental problems.
ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT
- Environmental impact assessment.
This should describe all of the ecological changes that the project could cause in the local area. There should also be an assessment of the economic and social repercussions of the project before any important decision are made.
- Effects on the environment.
· Extracting natural resources: fossil fuels and radioactive elements are extracted from underground deposits. Large areas of forets have been destroyed to provide wood for fuel.
· Transporting fuel: oil is transported over land through pipelines and by sea in oil tankers. Natural gas is transported over land through gas pipelines or by sea in tankers as liquid natural gas (LNG). Natural disasters can also affect it.
· Generating electricity: hydroelectric power stations require large amounts of water which must be stored in reservoirs. These changes have enormous effects on ecosystems alon the entire lenght of the river.
· Waste treatment: nuclear waste is kept in special containers which usually located underground or in deep ocean trenches. Deep ocean storage can be a problem if corrosion damages ythe containers and the radioactive waste escapes.
- Climate change.
The most serious negative effect on the environment is climate change.
· When we burn fossil fuels, gases such as carbon dioxide and methane are released into the air and contribute to the greenhouse effect.
· Global warming, such as the melting of our polar ice caps and glaciers which lead to rising sea levels.
· Acid rain is the combination of sulphur oxide and nitrous oxide, produced by the fossil fuels, and water vapour.
· Power stations affect plants and animals life because they use refrigeration systems that pump hot water into our rivers and oceans.
- Energy consumption.
The fossil fuels that consumers use in their cars or home heating systems also have an effect on the environment. The generation and transportation of electricity can have serious effects on the environment.
This should describe all of the ecological changes that the project could cause in the local area. There should also be an assessment of the economic and social repercussions of the project before any important decision are made.
- Effects on the environment.
· Extracting natural resources: fossil fuels and radioactive elements are extracted from underground deposits. Large areas of forets have been destroyed to provide wood for fuel.
· Transporting fuel: oil is transported over land through pipelines and by sea in oil tankers. Natural gas is transported over land through gas pipelines or by sea in tankers as liquid natural gas (LNG). Natural disasters can also affect it.
· Generating electricity: hydroelectric power stations require large amounts of water which must be stored in reservoirs. These changes have enormous effects on ecosystems alon the entire lenght of the river.
· Waste treatment: nuclear waste is kept in special containers which usually located underground or in deep ocean trenches. Deep ocean storage can be a problem if corrosion damages ythe containers and the radioactive waste escapes.
- Climate change.
The most serious negative effect on the environment is climate change.
· When we burn fossil fuels, gases such as carbon dioxide and methane are released into the air and contribute to the greenhouse effect.
· Global warming, such as the melting of our polar ice caps and glaciers which lead to rising sea levels.
· Acid rain is the combination of sulphur oxide and nitrous oxide, produced by the fossil fuels, and water vapour.
· Power stations affect plants and animals life because they use refrigeration systems that pump hot water into our rivers and oceans.
- Energy consumption.
The fossil fuels that consumers use in their cars or home heating systems also have an effect on the environment. The generation and transportation of electricity can have serious effects on the environment.
POWER STATIONS THAT USE RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES
Some power stations use clean, renewable energy sources to produce electricity. These alternatives help to reduce our dependence on non-renewable sources of energy, such as fossil fuels, which also cause environement problems.
- Wind farms.
Use the kinetic energy of the wind to generate electricity. The wind turns the blades of a turbine, at the top of a tower. The blades are cennected to a gearbox which increases the rotational speed of the generator.
The output and efficiency depend on two factors:
· The location of the farm, which determines the speed and strength of the winds.
· The numbers of turbines that can be installed there.
- Wind farms.
Use the kinetic energy of the wind to generate electricity. The wind turns the blades of a turbine, at the top of a tower. The blades are cennected to a gearbox which increases the rotational speed of the generator.
The output and efficiency depend on two factors:
· The location of the farm, which determines the speed and strength of the winds.
· The numbers of turbines that can be installed there.
- Hydroelectric power stations.
There are two types of hydroelectric power station.
· In conventional hydroelectric stations,the wáter flows from the reservoir to the turbines throungh a high-pressure conduit.Then it flows out,usually into a river.
·In pumped-storage hydroelectric stations,the water flows from the turbines to a second reservoir. Then it is pumped back up to the higher reservoir and stored for later.
-Solar power stations.
Use energy from sunlight to generate electricity.There are two main types of solar power stations:
· Solar thermal stations: with solar collectors that absorb sunlight in order to produce heat. With mirrors called heliostats that reflect and concéntrate sunlight in one place.
· Photovoltaic stations: solar panels convert sunlight directly into electricity. Small solar power installations can provide energy for homes and rural areas. Excess power can be stored in batteries or accumulators and used at night.
- Biomass power stations.
Biomass is an organic material that is produral processes.
In a biomass power station,the fuel used to produce energy comes from biomass. The steam produced from burning the biomass moves a turbine that is connected to a generator.
Biomass stations are efficient because they use waste materials that would normally end up in landfill sites.
- Marine power stations.
Use the movement of ocean water to generate electricity. There are three general types of marine power stations:
· Tidal power stations, which use the energy of tides.
· Wave power stations, which use the energy of waves.
· Ocean thermal conversion stations, which use the difference in water temperature between the surface of the ocean and deeper areas to produce energy.
- Geothermal power stations.
Use natural heat from the deepest underground layers of our planet. Can be used in two ways:
· It can be used directly to provide hot water for heating and industrial uses.
· It can be used indirectly to drive generators and produce electricity.
Tuesday, 14 March 2017
ELECTRIC POWER STATIONS THAT USE NON-RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES
- Thermal power stations.
Produce thermal energy.
Fossil fuels are used to heat water in a boiler, then the boiler turns a turbine, which is connected to the rotor of a generator and produces electricity and it is transported. After that the steam goes to a condenser and becomes liquid water again. Finally, the water is pumped back to the boiler.
In combined-cycle the electricity is genertaed in two systems.
· First system: burns natural gas with compressed air and this produce superheated gases.
· Second system: use the hot gases from the first system.
- Nuclear power stations.
Is a thermal power station that uses a nuclear reactor to produce heat. The reactor uses radioactive material such as uranium.
· Advantages: productivity and profitability.
· Disadvantages: the risks of nuclear accidents and the management and storage of radioactive waste.
Produce thermal energy.
Fossil fuels are used to heat water in a boiler, then the boiler turns a turbine, which is connected to the rotor of a generator and produces electricity and it is transported. After that the steam goes to a condenser and becomes liquid water again. Finally, the water is pumped back to the boiler.
In combined-cycle the electricity is genertaed in two systems.
· First system: burns natural gas with compressed air and this produce superheated gases.
· Second system: use the hot gases from the first system.
- Nuclear power stations.
Is a thermal power station that uses a nuclear reactor to produce heat. The reactor uses radioactive material such as uranium.
· Advantages: productivity and profitability.
· Disadvantages: the risks of nuclear accidents and the management and storage of radioactive waste.
ELECTRICAL ENERGY
Electrical energy is a form of energy that is transported by an electrical current. Is very common for two reasons:
· It can be easily transformed into other types of energy.
· It can be transported over long distances.
- Electric power stations.
A power station is a place where energy from natural resources is transformed into energy that we can consume. If the energy obtained is electricity, it is called an electrical power station. The electric power stations use generators to transform the energy. The generators are called alternators. Usually has a stationary part called stator and a moving part called a rotor. A turbine turns the axis of the rotor, which generates an alternating electric current.
- The transportation and distribution of electricity.
Electrical energy is transported from power stations to the places where it is needed.
The transportation includes:
· Raising the voltage: it must be transported over long distances, so the voltage is raised to avoid the loss of energy as heat.
· High voltage lines: the lines are installed on towers.
· Reducing the voltage: the substations are installed between high voltage lines and final consumers. Use transformers to reduce the power to lower voltages.
· Power is distributed to industries and urban areas.
· It can be easily transformed into other types of energy.
· It can be transported over long distances.
- Electric power stations.
A power station is a place where energy from natural resources is transformed into energy that we can consume. If the energy obtained is electricity, it is called an electrical power station. The electric power stations use generators to transform the energy. The generators are called alternators. Usually has a stationary part called stator and a moving part called a rotor. A turbine turns the axis of the rotor, which generates an alternating electric current.
- The transportation and distribution of electricity.
Electrical energy is transported from power stations to the places where it is needed.
The transportation includes:
· Raising the voltage: it must be transported over long distances, so the voltage is raised to avoid the loss of energy as heat.
· High voltage lines: the lines are installed on towers.
· Reducing the voltage: the substations are installed between high voltage lines and final consumers. Use transformers to reduce the power to lower voltages.
· Power is distributed to industries and urban areas.
ENERGY SOURCES
Energy sources are natural resources that we can use to generate different forms of energy. Then we can transform that in energy for various purposes.
We can classify into two general categories:
- Non-renewable energy sources.
Come from natural resources that are limitated and can be exhausted. Are the most commonly used. They include fossil fuels (oil, coal and natural gas), and nuclear energy, which uses radioactive materials.
- Renowable energy sources.
Come from natural resources that we cannot use up completely. These include solar, marine, hydroelectric, geothermal and biomass.
We can classify into two general categories:
- Non-renewable energy sources.
Come from natural resources that are limitated and can be exhausted. Are the most commonly used. They include fossil fuels (oil, coal and natural gas), and nuclear energy, which uses radioactive materials.
- Renowable energy sources.
Come from natural resources that we cannot use up completely. These include solar, marine, hydroelectric, geothermal and biomass.
ENERGY TRANSFORMATIONS
Energy can be transformed, but it cannot be created or destroyed. This is the principle of energy conservation.
For example: a battery contains chemical energy which is transformed into electrical energy or the chemical energy in our muscles can be transformed into mechanical energy.
For example: a battery contains chemical energy which is transformed into electrical energy or the chemical energy in our muscles can be transformed into mechanical energy.
Mechanical energy
ENERGY
Energy is the capacity of a body to perform transformations and do work.
In prehistoric times, muscular energy was the only source of energy that people had.
- Forms of energy.
· Potential: the height of an object above the ground.
· Kinetic: the energy of physical movement.
· Mechanical: the sum of potential and kinetic energy.
· Sound: the energy of sound waves.
· Electrical: electrical current.
· Nuclear: the energy in the nucleus of an atom.
· Luminous: asociated with lights.
· Thermal: asciated with the movement of particles in matter.
· Chemical: results from the formation or decomposition of substances.
· Electromagnetic: occurs when electrical currents create magnetic fields.
- Units of measurement for energy.
International System: joules (J).
When energy takes the form of heat, we express it as calories (cal).
1 cal = 4.18 J
-Power.
Power (P), expressed in watts, is a measurement of how quickly work is done.
The power of a machine is the amount of work (W), expressed in joules, that it can do in a certain amount of time (t), expressed in seconds (s).
Energy conversion efficiency (%) = output/input · 100
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)